Printed from www.flong.com/texts/code/shapers_circ/
Contents © 2020 Golan Levin and Collaborators
Golan Levin and Collaborators
Code
- Peer-Reviewed Publications
- Essays and Statements
- Interviews and Dialogues
- Catalogues and Lists
- Project Reports
- Press Clippings
- Lectures
- Code
- Misc.
- 07 2006. Shaping Functions: Polynomial
- 07 2006. Shaping Functions: Exponential
- 07 2006. Shaping Functions: Circular and Elliptical
- 07 2006. Shaping Functions: Bezier and Parametric
Circular & Elliptical Shaping Functions
- Circular Interpolation: Ease-In and Ease-Out
- Double-Circle Seat
- Double-Circle Sigmoid
- Double-Elliptic Seat
- Double-Elliptic Sigmoid
- Double-Linear with Circular Fillet
- Circular Arc Through a Given Point
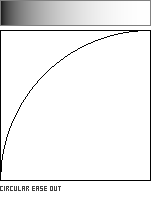
Circular Interpolation: Ease-In and Ease-Out
A circular arc offers a quick and easy-to-code method for easing in or out of the unit square. The computational efficiency of the function is diminished by its use of a square root, however.
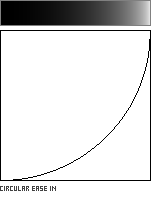
Ease-In interpolation:
![]()
Ease-Out interpolation:
![]()
//------------------------------
float circularEaseIn (float x){
float y = 1 - sqrt(1 - x*x);
return y;
}
//------------------------------
float circularEaseOut (float x){
float y = sqrt(1 - sq(1 - x));
return y;
}
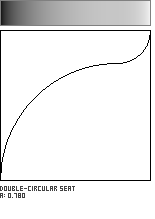
Double-Circle Seat
This shaping function is formed by the meeting of two circular arcs, which join with a horizontal tangent. The parameter a, in the range [0...1], governs the location of the curve's inflection point along the diagonal of the unit square.
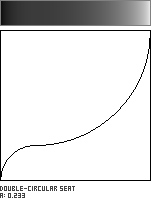
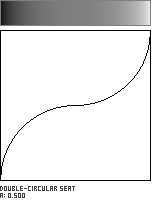
![]()
![]()
//----------------------------------------
float doubleCircleSeat (float x, float a){
float min_param_a = 0.0;
float max_param_a = 1.0;
a = max(min_param_a, min(max_param_a, a));
float y = 0;
if (x<=a){
y = sqrt(sq(a) - sq(x-a));
} else {
y = 1 - sqrt(sq(1-a) - sq(x-a));
}
return y;
}
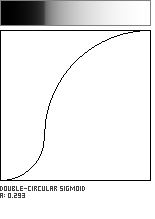
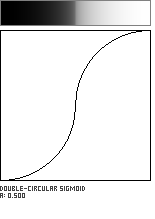
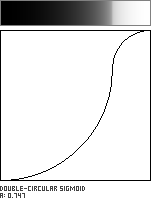
Double-Circle Sigmoid
This sigmoidal shaping function is formed by the meeting of two circular arcs, which join with a vertical tangent. The parameter a, in the range [0...1], governs the location of the curve's inflection point along the diagonal of the unit square.
![]()
![]()
//-------------------------------------------
float doubleCircleSigmoid (float x, float a){
float min_param_a = 0.0;
float max_param_a = 1.0;
a = max(min_param_a, min(max_param_a, a));
float y = 0;
if (x<=a){
y = a - sqrt(a*a - x*x);
} else {
y = a + sqrt(sq(1-a) - sq(x-1));
}
return y;
}
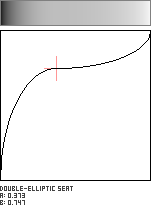
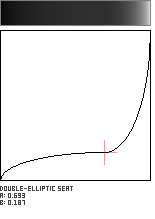
Double-Elliptic Seat
This seat-shaped function is created by the joining of two elliptical arcs, and is a generalization of the Double-Circle Seat. The two arcs meet at the coordinate (a,b) with a horizontal tangent.
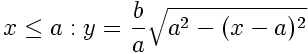
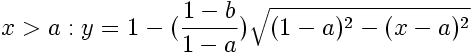
//---------------------------------------------------
float doubleEllipticSeat (float x, float a, float b){
float epsilon = 0.00001;
float min_param_a = 0.0 + epsilon;
float max_param_a = 1.0 - epsilon;
float min_param_b = 0.0;
float max_param_b = 1.0;
a = max(min_param_a, min(max_param_a, a));
b = max(min_param_b, min(max_param_b, b));
float y = 0;
if (x<=a){
y = (b/a) * sqrt(sq(a) - sq(x-a));
} else {
y = 1- ((1-b)/(1-a))*sqrt(sq(1-a) - sq(x-a));
}
return y;
}
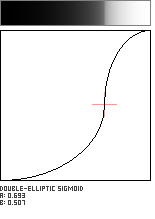
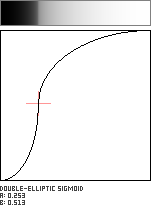
Double-Elliptic Sigmoid
This sigmoid-shaped function is created by the joining of two elliptical arcs, and is a generalization of the Double-Circle Sigmoid. The arcs meet at the coordinate (a, b) in the unit square with a vertical tangent.
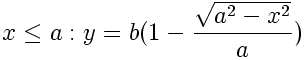
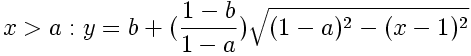
//------------------------------------------------------
float doubleEllipticSigmoid (float x, float a, float b){
float epsilon = 0.00001;
float min_param_a = 0.0 + epsilon;
float max_param_a = 1.0 - epsilon;
float min_param_b = 0.0;
float max_param_b = 1.0;
a = max(min_param_a, min(max_param_a, a));
b = max(min_param_b, min(max_param_b, b));
float y = 0;
if (x<=a){
y = b * (1 - (sqrt(sq(a) - sq(x))/a));
} else {
y = b + ((1-b)/(1-a))*sqrt(sq(1-a) - sq(x-1));
}
return y;
}
Double-Linear with Circular Fillet
This pattern joins two straight lines with a circular arc whose radius is adjustable. The user specifies the fillet's radius (with parameter c) and the coordinate in the unit square where the lines would otherwise intersect (with parameters a and b). This pattern is adapted from Robert D. Miller's "Joining Two Lines with a Circular Arc Fillet", which appears in Graphics Gems III.
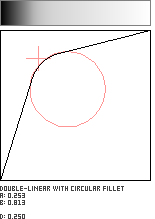
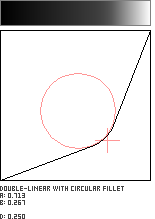
//--------------------------------------------------------
// Joining Two Lines with a Circular Arc Fillet
// Adapted from Robert D. Miller / Graphics Gems III.
float arcStartAngle;
float arcEndAngle;
float arcStartX, arcStartY;
float arcEndX, arcEndY;
float arcCenterX, arcCenterY;
float arcRadius;
//--------------------------------------------------------
float circularFillet (float x, float a, float b, float R){
float epsilon = 0.00001;
float min_param_a = 0.0 + epsilon;
float max_param_a = 1.0 - epsilon;
float min_param_b = 0.0 + epsilon;
float max_param_b = 1.0 - epsilon;
a = max(min_param_a, min(max_param_a, a));
b = max(min_param_b, min(max_param_b, b));
computeFilletParameters (0,0, a,b, a,b, 1,1, R);
float t = 0;
float y = 0;
x = max(0, min(1, x));
if (x <= arcStartX){
t = x / arcStartX;
y = t * arcStartY;
} else if (x >= arcEndX){
t = (x - arcEndX)/(1 - arcEndX);
y = arcEndY + t*(1 - arcEndY);
} else {
if (x >= arcCenterX){
y = arcCenterY - sqrt(sq(arcRadius) - sq(x-arcCenterX));
} else{
y = arcCenterY + sqrt(sq(arcRadius) - sq(x-arcCenterX));
}
}
return y;
}
//------------------------------------------
// Return signed distance from line Ax + By + C = 0 to point P.
float linetopoint (float a, float b, float c, float ptx, float pty){
float lp = 0.0;
float d = sqrt((a*a)+(b*b));
if (d != 0.0){
lp = (a*ptx + b*pty + c)/d;
}
return lp;
}
//------------------------------------------
// Compute the parameters of a circular arc
// fillet between lines L1 (p1 to p2) and
// L2 (p3 to p4) with radius R.
//
void computeFilletParameters (
float p1x, float p1y,
float p2x, float p2y,
float p3x, float p3y,
float p4x, float p4y,
float r){
float c1 = p2x*p1y - p1x*p2y;
float a1 = p2y-p1y;
float b1 = p1x-p2x;
float c2 = p4x*p3y - p3x*p4y;
float a2 = p4y-p3y;
float b2 = p3x-p4x;
if ((a1*b2) == (a2*b1)){ /* Parallel or coincident lines */
return;
}
float d1, d2;
float mPx, mPy;
mPx = (p3x + p4x)/2.0;
mPy = (p3y + p4y)/2.0;
d1 = linetopoint(a1,b1,c1,mPx,mPy); /* Find distance p1p2 to p3 */
if (d1 == 0.0) {
return;
}
mPx = (p1x + p2x)/2.0;
mPy = (p1y + p2y)/2.0;
d2 = linetopoint(a2,b2,c2,mPx,mPy); /* Find distance p3p4 to p2 */
if (d2 == 0.0) {
return;
}
float c1p, c2p, d;
float rr = r;
if (d1 <= 0.0) {
rr= -rr;
}
c1p = c1 - rr*sqrt((a1*a1)+(b1*b1)); /* Line parallel l1 at d */
rr = r;
if (d2 <= 0.0){
rr = -rr;
}
c2p = c2 - rr*sqrt((a2*a2)+(b2*b2)); /* Line parallel l2 at d */
d = (a1*b2)-(a2*b1);
float pCx = (c2p*b1-c1p*b2)/d; /* Intersect constructed lines */
float pCy = (c1p*a2-c2p*a1)/d; /* to find center of arc */
float pAx = 0;
float pAy = 0;
float pBx = 0;
float pBy = 0;
float dP,cP;
dP = (a1*a1) + (b1*b1); /* Clip or extend lines as required */
if (dP != 0.0){
cP = a1*pCy - b1*pCx;
pAx = (-a1*c1 - b1*cP)/dP;
pAy = ( a1*cP - b1*c1)/dP;
}
dP = (a2*a2) + (b2*b2);
if (dP != 0.0){
cP = a2*pCy - b2*pCx;
pBx = (-a2*c2 - b2*cP)/dP;
pBy = ( a2*cP - b2*c2)/dP;
}
float gv1x = pAx-pCx;
float gv1y = pAy-pCy;
float gv2x = pBx-pCx;
float gv2y = pBy-pCy;
float arcStart = (float) atan2(gv1y,gv1x);
float arcAngle = 0.0;
float dd = (float) sqrt(((gv1x*gv1x)+(gv1y*gv1y)) * ((gv2x*gv2x)+(gv2y*gv2y)));
if (dd != (float) 0.0){
arcAngle = (acos((gv1x*gv2x + gv1y*gv2y)/dd));
}
float crossProduct = (gv1x*gv2y - gv2x*gv1y);
if (crossProduct < 0.0){
arcStart -= arcAngle;
}
float arc1 = arcStart;
float arc2 = arcStart + arcAngle;
if (crossProduct < 0.0){
arc1 = arcStart + arcAngle;
arc2 = arcStart;
}
arcCenterX = pCx;
arcCenterY = pCy;
arcStartAngle = arc1;
arcEndAngle = arc2;
arcRadius = r;
arcStartX = arcCenterX + arcRadius*cos(arcStartAngle);
arcStartY = arcCenterY + arcRadius*sin(arcStartAngle);
arcEndX = arcCenterX + arcRadius*cos(arcEndAngle);
arcEndY = arcCenterY + arcRadius*sin(arcEndAngle);
}
Circular Arc Through a Given Point
This function defines a circular arc which passes through a user-specified point in the unit square. Unfortunately, not every location in the unit square lends itself to defining a circle which also is confined to the unit square; the user-supplied point must inhabit a zone close to the main (Identity) diagonal. This pattern is adapted from Paul Bourke's Equation of a Circle From 3 Points.
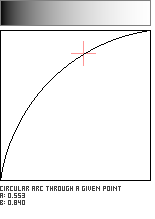
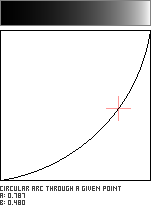
//---------------------------------------------------------
// Adapted from Paul Bourke
float m_Centerx;
float m_Centery;
float m_dRadius;
float circularArcThroughAPoint (float x, float a, float b){
float epsilon = 0.00001;
float min_param_a = 0.0 + epsilon;
float max_param_a = 1.0 - epsilon;
float min_param_b = 0.0 + epsilon;
float max_param_b = 1.0 - epsilon;
a = min(max_param_a, max(min_param_a, a));
b = min(max_param_b, max(min_param_b, b));
x = min(1.0-epsilon, max(0.0+epsilon, x));
float pt1x = 0;
float pt1y = 0;
float pt2x = a;
float pt2y = b;
float pt3x = 1;
float pt3y = 1;
if (!IsPerpendicular(pt1x,pt1y, pt2x,pt2y, pt3x,pt3y))
calcCircleFrom3Points (pt1x,pt1y, pt2x,pt2y, pt3x,pt3y);
else if (!IsPerpendicular(pt1x,pt1y, pt3x,pt3y, pt2x,pt2y))
calcCircleFrom3Points (pt1x,pt1y, pt3x,pt3y, pt2x,pt2y);
else if (!IsPerpendicular(pt2x,pt2y, pt1x,pt1y, pt3x,pt3y))
calcCircleFrom3Points (pt2x,pt2y, pt1x,pt1y, pt3x,pt3y);
else if (!IsPerpendicular(pt2x,pt2y, pt3x,pt3y, pt1x,pt1y))
calcCircleFrom3Points (pt2x,pt2y, pt3x,pt3y, pt1x,pt1y);
else if (!IsPerpendicular(pt3x,pt3y, pt2x,pt2y, pt1x,pt1y))
calcCircleFrom3Points (pt3x,pt3y, pt2x,pt2y, pt1x,pt1y);
else if (!IsPerpendicular(pt3x,pt3y, pt1x,pt1y, pt2x,pt2y))
calcCircleFrom3Points (pt3x,pt3y, pt1x,pt1y, pt2x,pt2y);
else {
return 0;
}
// constrain
if ((m_Centerx > 0) && (m_Centerx < 1)){
if (a < m_Centerx){
m_Centerx = 1;
m_Centery = 0;
m_dRadius = 1;
} else {
m_Centerx = 0;
m_Centery = 1;
m_dRadius = 1;
}
}
float y = 0;
if (x >= m_Centerx){
y = m_Centery - sqrt(sq(m_dRadius) - sq(x-m_Centerx));
} else {
y = m_Centery + sqrt(sq(m_dRadius) - sq(x-m_Centerx));
}
return y;
}
//----------------------
boolean IsPerpendicular(
float pt1x, float pt1y,
float pt2x, float pt2y,
float pt3x, float pt3y)
{
// Check the given point are perpendicular to x or y axis
float yDelta_a = pt2y - pt1y;
float xDelta_a = pt2x - pt1x;
float yDelta_b = pt3y - pt2y;
float xDelta_b = pt3x - pt2x;
float epsilon = 0.000001;
// checking whether the line of the two pts are vertical
if (abs(xDelta_a) <= epsilon && abs(yDelta_b) <= epsilon){
return false;
}
if (abs(yDelta_a) <= epsilon){
return true;
}
else if (abs(yDelta_b) <= epsilon){
return true;
}
else if (abs(xDelta_a)<= epsilon){
return true;
}
else if (abs(xDelta_b)<= epsilon){
return true;
}
else return false;
}
//--------------------------
void calcCircleFrom3Points (
float pt1x, float pt1y,
float pt2x, float pt2y,
float pt3x, float pt3y)
{
float yDelta_a = pt2y - pt1y;
float xDelta_a = pt2x - pt1x;
float yDelta_b = pt3y - pt2y;
float xDelta_b = pt3x - pt2x;
float epsilon = 0.000001;
if (abs(xDelta_a) <= epsilon && abs(yDelta_b) <= epsilon){
m_Centerx = 0.5*(pt2x + pt3x);
m_Centery = 0.5*(pt1y + pt2y);
m_dRadius = sqrt(sq(m_Centerx-pt1x) + sq(m_Centery-pt1y));
return;
}
// IsPerpendicular() assure that xDelta(s) are not zero
float aSlope = yDelta_a / xDelta_a;
float bSlope = yDelta_b / xDelta_b;
if (abs(aSlope-bSlope) <= epsilon){
// checking whether the given points are colinear.
return;
}
// calc center
m_Centerx = (
aSlope*bSlope*(pt1y - pt3y) +
bSlope*(pt1x + pt2x) -
aSlope*(pt2x+pt3x) )
/(2* (bSlope-aSlope) );
m_Centery = -1*(m_Centerx - (pt1x+pt2x)/2)/aSlope + (pt1y+pt2y)/2;
m_dRadius = sqrt(sq(m_Centerx-pt1x) + sq(m_Centery-pt1y));
}